What is a bot? Are bots dangerous? Everything you need to know
Bots are playing an increasingly large part in many areas of online activity. You can find them in social media, online stores, customer support systems, and numerous other places, carrying out their pre-programmed tasks and routines.
However, while some bots are helpful, others can cause serious harm, from spreading malware to launching scams and stealing data. This guide looks at what bots are, how they work, what makes a bot good or bad, and how to detect and prevent malicious bot activity.
What is a bot?
The term “bot” is short for “robot” and refers to a computer program or algorithm designed to perform certain tasks on its own, without the need for manual oversight and intervention.
Bots often perform tasks typically handled by humans, doing them much faster and more efficiently.
Some examples of tasks that bots carry out are automated messaging, performance monitoring, and reporting, but their uses are almost endless.
How do bots work?
Bots work by simply following their programming. They’re often designed with strict rulesets or algorithms that essentially tell them what to do, dictating the tasks they carry out and their actions or reactions in certain situations. Once programmed, bots can operate independently, carrying out their tasks without continuous human oversight.
A lot of bots also work together, operating over networks and communicating with other bots via the likes of instant messaging services. However, the exact processes each bot executes differ from one to the next, and some are much more advanced than others, using AI and machine learning technologies to execute a broader range of functions.
As an example of bots in action, we can look at customer service chatbots. Many of these are programmed with rule-based algorithms, where they give the user a series of possible options and generate responses based on what the user selects. Others are more intelligent and use AI to respond more dynamically to user queries, but both fulfill the same fundamental role.
Types of bots: Good bots vs. bad bots
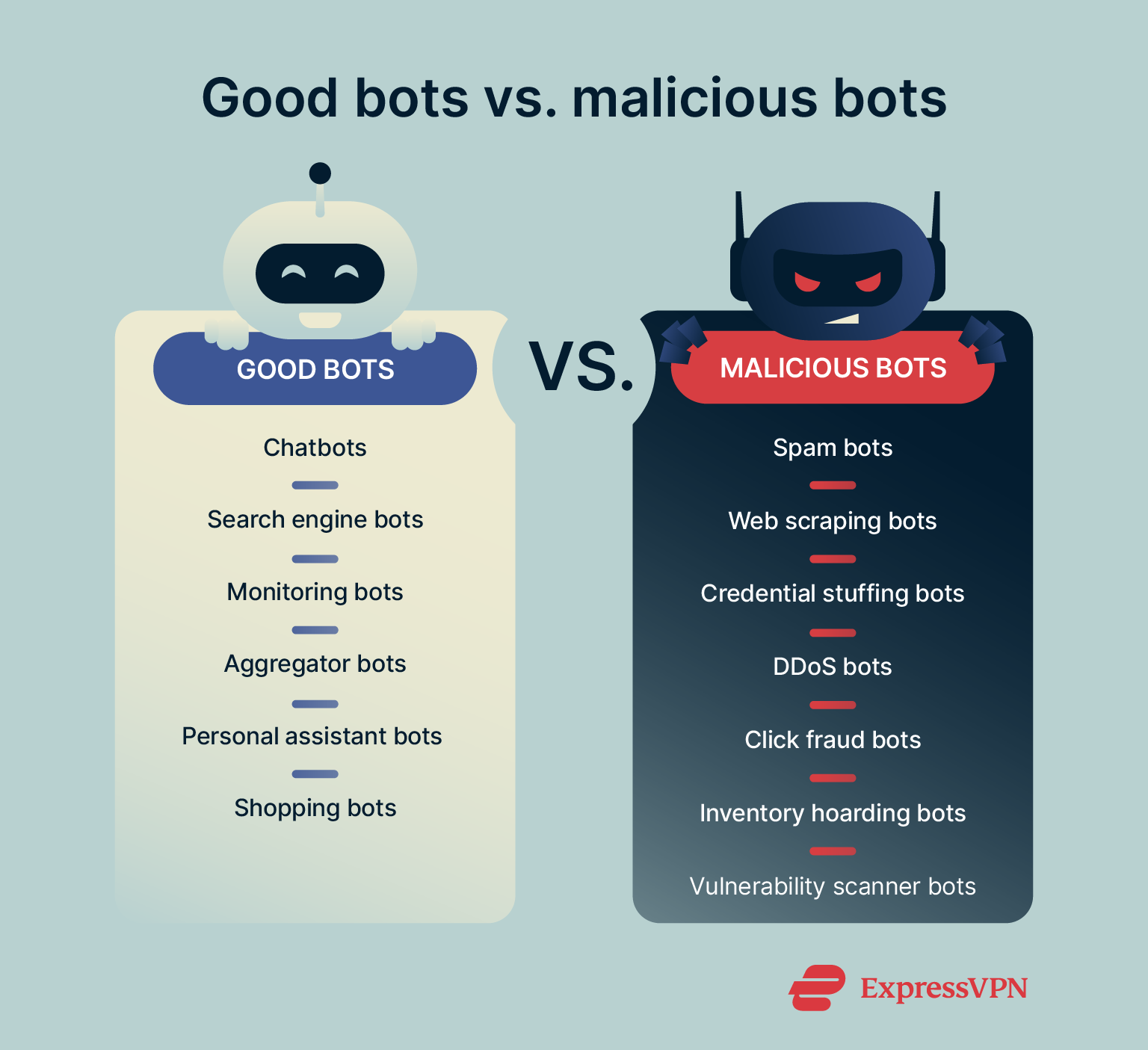
Good bots
These bots are designed to help people, to serve customers, and to make life easier for those who use them.
Chatbots
As their name implies, chatbots are designed to chat with people. They can carry out conversations, respond to questions, and provide useful information to those who need it. They’re often employed in fields like customer service, helping users get quick answers to common questions without needing to contact a human support worker.
Banks, online stores, and many other websites use chatbots, and they vary in “intelligence” and complexity. Basic ones simply follow sets of predefined rules and give pre-written responses, while advanced AI chatbots can understand more conversational nuances and generate their own unique replies.
While chatbots have many legitimate purposes, it’s worth noting that, like all bots, in the wrong hands they can also be used maliciously. Some negative uses for chatbots include harassment, bullying, or spreading misinformation.
Web crawlers (search engine bots)
Web crawlers, sometimes known as spider bots or search engine bots, play a very important behind-the-scenes role in search engines like Google and Bing. They scour the web, reading and analyzing the content of webpages, including text, images, links, and metadata, and index the information they find in the search engine’s database.
Search engines then use that data to provide relevant results when users type in their queries and search terms. In other words, it’s thanks to these bots that you can google something and, in many cases, quickly find what you’re looking for.
Monitoring bots
Monitoring bots track, monitor, and observe websites, systems, or servers. They collect data and keep an eye on performance metrics, issuing alerts if they detect any problems, changes, or abnormalities. They’re often used by online businesses to monitor product prices or stock prices, keeping their users informed of any big price shifts up or down.
Aggregator bots
Aggregator bots collate information. They can scour different sources to find relevant data for a user, organize and categorize their findings, and then deliver those findings in a convenient, accessible format.
An example of this would be a news aggregator bot, which can collect interesting news stories and headlines from various sources to present in a user’s feed.
Personal assistant bots
These bots fulfil many of the duties a real-life personal assistant might do, like managing calendars, scheduling, issuing reminders about key times and dates, gathering information, and answering questions. They can be used in both professional and personal settings, and are largely powered by AI.
Examples of these bots include Siri and Alexa, which many people use at home to do things like checking the weather forecast, playing music, or learning about the latest news headlines.
Shopping bots
Shopping bots, or shopbots, scan the internet in search of specific products, aiming to find the best possible price for the user. They can compare prices from numerous sources, find deals and promotions, provide product reviews, and track pricing history. This all helps customers make smarter purchases.
They share some functions with aggregator bots, but they also have extra functions that are shopping-oriented, like helping users find specific products to fit their needs and complete their orders.
Malicious bots
Unfortunately, not all bots are used to help people. Some bot programmers have much more devious ends in mind and use bots to trick, scam, and steal.
Spam bots
The purpose of spam bots is to spread spam, which is unwanted or unsolicited digital messages or content, often far and wide in great quantities. These bots are typically able to scrape information, like contact details, from the internet.
They can then use that in two distinct ways: firstly, to make fake profiles for spreading spam on social media, and secondly, to deliver spam messages to the email addresses they find.
People and organizations can use spam bots to spread misinformation, dishonest advertisements, links to malicious sites, and more.
Web scraping bots
Web scraping bots are quite similar to search engine or spider bots. They’re able to scan the internet to find and analyze data. However, they go a step further than that; instead of just reading and using parts of the data, scrapers can download all the content of a website, which is often illegal or violates site terms and conditions.
These bots can then take site data to be republished elsewhere, like copying blogs and articles, or copy product databases to set up online stores using stolen data. This can cause indexing problems on search engines, damage site reputations, and confuse users.
Credential stuffing bots
These bots take login data, like usernames and passwords, which may have been found out through data leaks or breaches. They then use that data to systematically attempt to log in on multiple sites and services, including major platforms like Amazon and Facebook. They can test thousands of credentials incredibly quickly across numerous websites.
Cybercriminals use these bots to gain access to people’s private accounts and data, which they can use in various ways, such as exploiting the accounts themselves or selling the logins their bots discover on dark web marketplaces. To guard against this kind of threat, you can use a tool like ExpressVPN’s ID Alerts to alert you if your data appears on the dark web (please note that ID Alerts is only available for U.S. users).
DDoS bots
DDoS stands for distributed denial of service. It’s a type of cyberattack in which lots of malicious traffic floods a target network. The aim is to saturate and incapacitate that network, forcing sites to go down or malfunction. This can lead to financial loss and reputation damage for the site owner.
Bots are vital for carrying out these attacks; hackers infect many devices with malicious bots to form large groups known as botnets. They can then activate their botnets as and when they want to launch their attacks, and the bigger the botnet, the more damaging the attack can be.
Click fraud bots
These bots carry out a very simple task: clicking on things. They click on online ads, especially those that work on a pay-per-click basis. That means the company that makes the ads pays every time someone clicks them. Malicious users exploit this to make their competitors spend more on their ads, thus draining their finances.
These bots can also interfere with a company’s marketing campaigns, skewing the data so they don’t know how effective their ads truly are.
Inventory hoarding bots
These bots make purchases or pre-orders of particular products, especially high-demand items like brand new video game consoles or limited edition sneakers. The idea here is that the bots buy up large quantities of these valuable items, which the bot owner can then sell on for a huge profit.
Vulnerability scanner bots
These bots scan systems and networks for weaknesses to exploit, making life much easier for cybercriminals. Instead of having to dig through pages of code themselves, they can let their bots find the weak points and then work their way into a network or piece of software to commit crimes like stealing data or infecting devices with malware.
While vulnerability scanners can be misused by cybercriminals, they are also valuable tools for security professionals seeking to patch weaknesses before they are exploited.
Real-world examples of bots in action
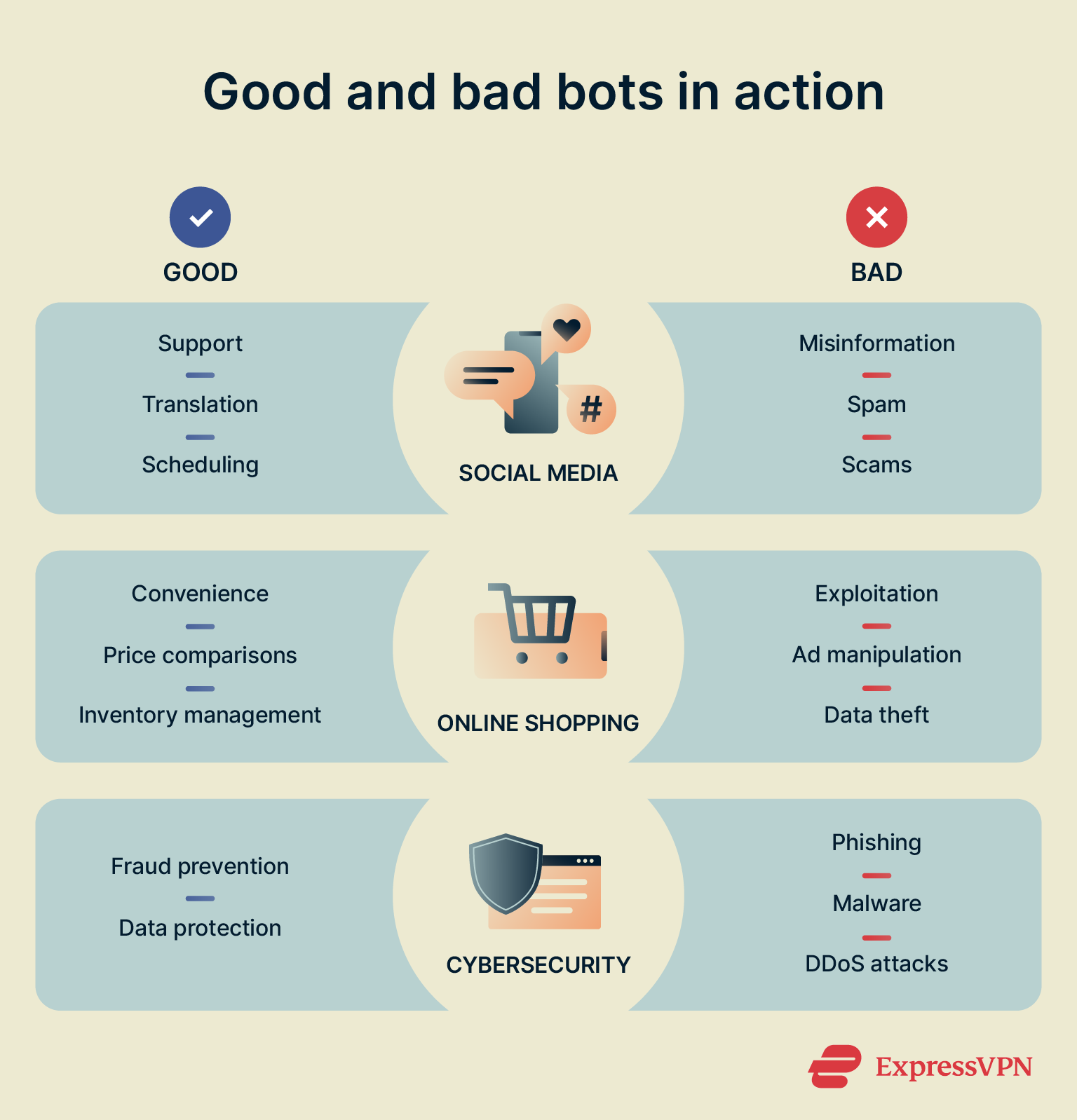
How bots are used in social media
Bots have many uses on social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, and X, some good, some bad. Many of the big platforms, for instance, have support bots that help answer common questions or troubleshoot account issues. Social media bots can also help with post scheduling and automation, saving users time, or with translating content into different languages.
However, there are also many darker sides to bot usage on social platforms. Bot accounts can spread spam, ads, hate speech, and misinformation, for instance, shaping online discourse and adding fuel to arguments and “flame wars.” They can also trick or scam people in various ways, by pretending to be people they’re not or by sharing malicious links.
Bots can also artificially boost the engagement or popularity of certain posts or users. Some people, for instance, purchase bots to boost their friend or follower counts, making them appear more popular and potentially giving them more influence than they deserve.
How bots impact e-commerce and online shopping
Just like social media, the world of online shopping also has positive and negative bots. On the plus side, bots can help users find the products they want faster, more conveniently, and at the best prices. They solve account issues and provide on-demand support for users, while allowing store owners to manage inventory, maintain competitive pricing, and spot fraud.
On the downside, some bots exploit online marketplaces, buying up large amounts of in-demand items to resell, damaging companies financially through ad click manipulation, scraping and stealing page data, and even writing and posting fake reviews or ratings to affect a store’s reputation.
Cybersecurity: Bots in attack and defense
Bots have many malicious uses in hacking and cyberattacks. They can be used to launch DDoS attacks and take entire sites and networks offline temporarily, as well as for stealing user data, conducting scams, and spreading malware. As they become more advanced and integrate AI, their potential to do damage and harm people only increases.
Fortunately, bots can also be used to counter cyberattacks and bolster defenses. Some bots are used in the financial sector, for example, to monitor suspicious activity and spot signs of fraud. They can also alert users about data breaches and leaks, guard against web scraping, mitigate DDoS attacks, and scan emails to let users know about possible phishing attempts.
Advantages and disadvantages of bots
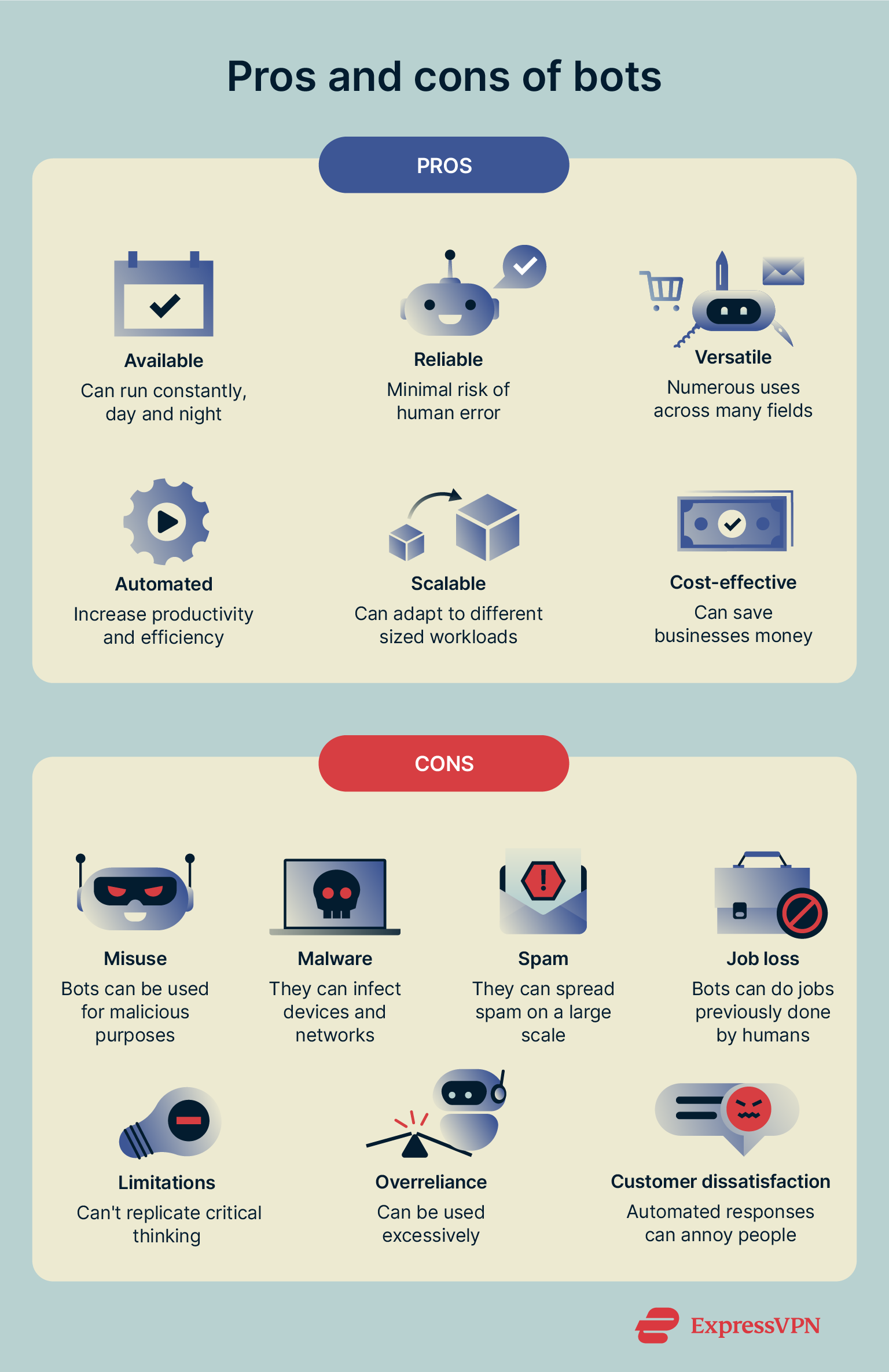 As shown throughout this guide, bots aren’t all good or all bad. They bring both benefits and downsides, and it’s important to acknowledge both sides of the equation to help us get value from bots while remaining aware of the risks they pose.
As shown throughout this guide, bots aren’t all good or all bad. They bring both benefits and downsides, and it’s important to acknowledge both sides of the equation to help us get value from bots while remaining aware of the risks they pose.
Benefits of bots
- Available: Bots can run 24/7, 365 days a year. They don’t need time off.
- Reliable: They can be trusted to carry out their programmed duties again and again in the exact same way, without human error or differing standards of quality.
- Versatile: They have a vast range of applications across many industries.
- Automated: They can automate tasks that would usually demand lots of human labor, helping with efficiency and productivity.
- Scalable: They can take on bigger or smaller workloads, as needed, with no fuss.
- Cost-effective: They can save businesses money on labor and resources.
Risks of bots
- Misuse: There are numerous ways bots can be misused for malicious ends.
- Malware: Bots are capable of spreading malware and carrying out cyberattacks.
- Spam and scams: Bots can spread spam and conduct automated scams.
- Job loss: In some cases, bots do jobs that people would have previously done.
- Limitations: Even the most advanced AI bots have limitations and cannot completely replicate human behavior and critical thinking.
- Overreliance: Excessive use of bots may lead to people failing to develop their own problem-solving skills and solutions.
- Customer dissatisfaction: Some people don’t enjoy engaging with support bots and prefer interacting with real customer support reps.
How to detect and prevent malicious bots
Given the many malicious ways in which bots can be used, it’s important to be able to spot bad bot behavior and prevent it where possible. There are many ways that everyday users can spot the signs of malicious bot activity and take protective measures.
Signs that a bot is interacting with you
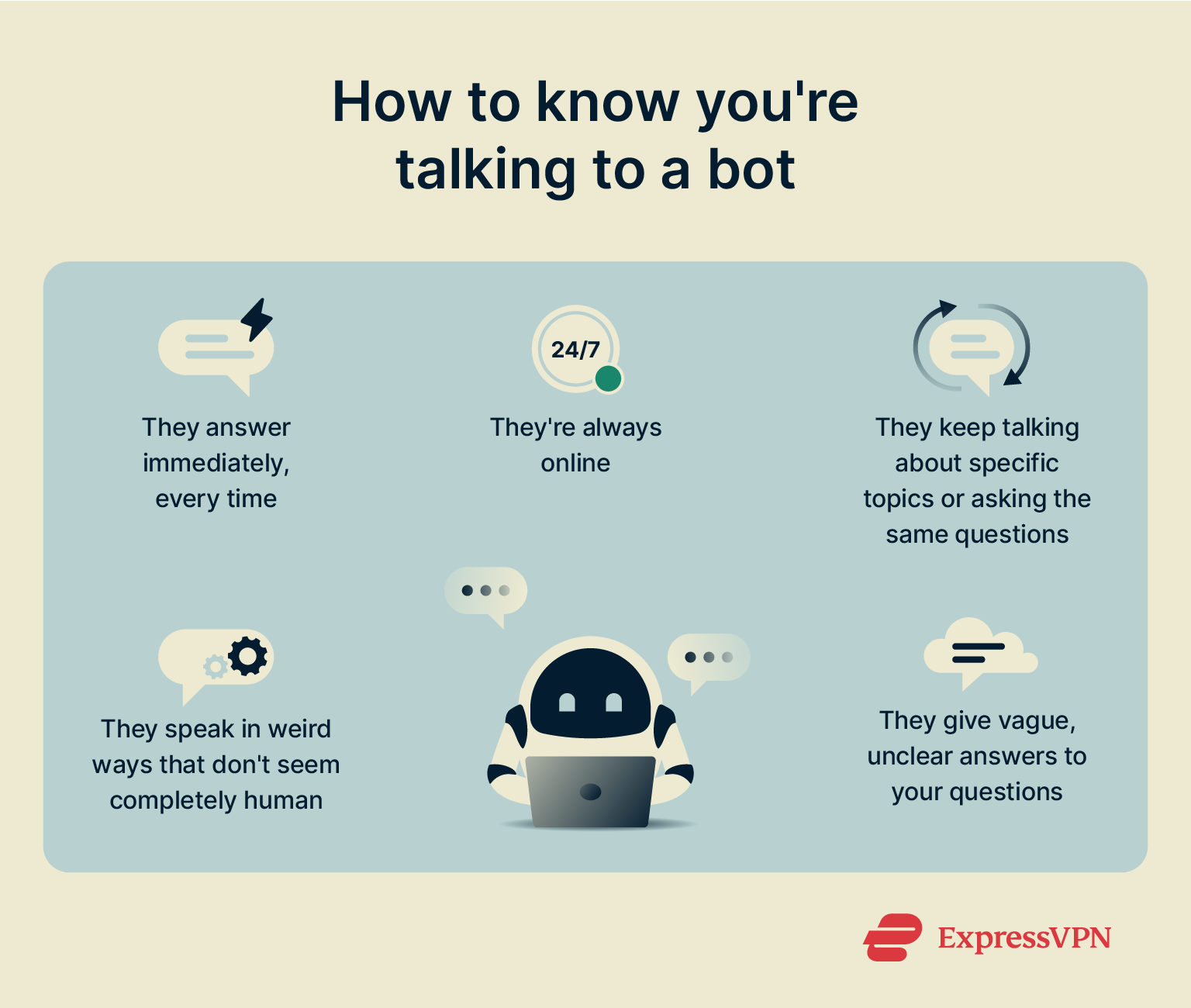 Look for these signs to spot when you might be chatting with a bot on social media or elsewhere:
Look for these signs to spot when you might be chatting with a bot on social media or elsewhere:
- Instant or near-instant replies to your messages
- Always online and available to chat
- Constantly driving the conversation to one particular topic
- Repetition of certain phrases or questions
- Unusual or unnatural word choices or sentence structures
- Vague or unclear answers
Common methods to identify and prevent malicious bots
Numerous methods exist to spot bad bots so that action can be taken to stop them in their tracks or guard against their malicious activities.
Traffic trends and anomalies
Good bots and other tools can be used to monitor internet traffic patterns and look for any abnormalities or signs of impending bot attacks. For example, if a website suddenly sees spikes in activity, it’s likely that botnets could be targeting it.
Site owners can keep a close eye on activity metrics or even configure alerts to let them know when suspected bot activity occurs.
Suspicious IPs and server load issues
Site owners may also notice that users with suspicious IP addresses, or IPs that have a history of spam and hacking attempts, are targeting their sites or pages. Sudden increases in server load, too, can be driven by bot activities like web scraping or DDoS attacks.
Again, tools exist to counter this, like bot detection and IP monitoring tools, which can blacklist suspected bot IPs automatically and detect non-human interactions, like very rapid clicks, to stop certain malicious bot activities.
CAPTCHA and bot filtering systems
CAPTCHA and similar bot filtering systems are designed to catch out bots and prevent them from accessing sites and services. These systems force the user to do something that would be hard for a bot, like entering a series of numbers or clicking a specific shape or symbol in an image.
However, as bots get smarter and begin to incorporate image recognition, CAPTCHAs are becoming less effective, and they’re no longer considered sufficient on their own to block bot activities.
FAQ: Common questions about bots
What is an example of a bot?
What do people use bots for?
Are bots always bad?
How can I tell if a website is using bots?
What are the most dangerous bots on the internet?
How can companies protect themselves from malicious bots?
What does bot mean in social media?
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN