Static IP vs. dynamic IP: Key differences, pros and cons, and which one you need

When you connect to the internet, your device gets an IP address, but did you know there are different types? Static and dynamic IPs might sound like tech jargon, but they play a big role in how you connect, stream, game, or set up a home server.
Whether you’re just curious or trying to figure out which one suits your needs, this guide breaks down the key differences, pros and cons, and when it actually matters which type you have.
What is an IP address, and how does it work?
Every device that connects to a network, whether it’s your phone, laptop, or smart fridge, gets an IP address. Think of it like a digital home address. It helps your device send and receive information, sometimes across the internet and sometimes just within your local network.
When you open a website, your device uses an IP address to locate the site, and the site uses your IP to send the right data (like the page content) back to you.
There are two main types of IP addresses:
- Private IP address: This is the IP your device uses within your local network. It’s assigned by your router and helps your devices talk to each other internally. For example, if you’re sending a document from your laptop to your printer, that data travels over private IPs. No need for the internet to get involved.
- Public IP address: This is the address your entire network uses to connect to the internet. It’s assigned by your internet service provider (ISP), and it’s what websites or streaming platforms see when your device makes a request, like loading a video or visiting a page.
And here’s where it gets interesting: public IPs can be static and dynamic. These labels describe whether your IP stays the same over time or changes regularly. We’ll dig into the details in a bit.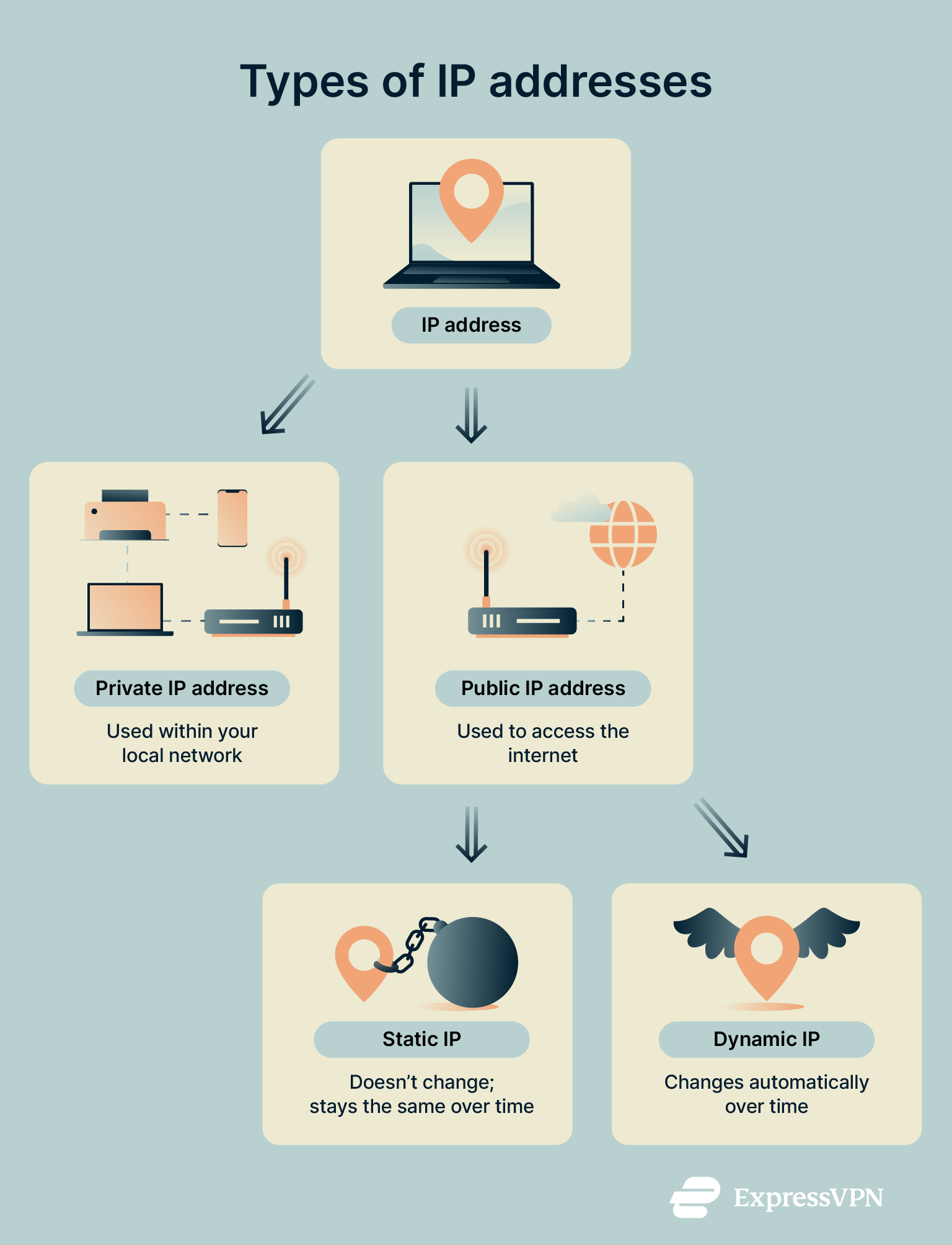 Note: Private IP addresses can also be static or dynamic. Your router might give your device the same address every time or assign a different one from a pool. But unlike public IPs, this usually doesn’t make much of a difference, since it only affects how devices connect within your home network.
Note: Private IP addresses can also be static or dynamic. Your router might give your device the same address every time or assign a different one from a pool. But unlike public IPs, this usually doesn’t make much of a difference, since it only affects how devices connect within your home network.
Understanding how IP addresses are assigned
Both private and public IP addresses can be assigned in two ways: automatically or manually. It depends on how the network is set up.
Let’s start with private IPs. When you connect a device to your home Wi-Fi, your router automatically assigns it a private IP address from a specific range using a system called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
These private IP ranges are reserved for internal use and defined by the RFC 1918 standard. Devices using these addresses can communicate within the same local network, but they can’t be reached directly from the internet. The three reserved ranges are:
- 10.0.0.0–10.255.255.255 (commonly used in larger networks)
- 172.16.0.0–172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0–192.168.255.255 (most common in home networks)
These ranges are reused across many networks, which is totally fine, since private IPs only work within your specific network. That’s why two different homes can have devices with the same private IPs without causing any conflict.
Note: DHCP is widely used because it’s convenient and automatic, but it’s not the only option. Some networks manually assign static IP addresses to specific devices, especially when consistent addressing is needed (like for printers or servers).
Now onto public IPs, which are assigned by your ISP:
- Dynamic public IP: Most people have this by default. Your ISP assigns you an IP from its available pool, and it may change from time to time, say, if you restart your router or after a certain lease period.
- Static public IP: This is manually set and doesn’t change unless someone changes it on purpose. Businesses often use static IPs to run servers or services that need to stay reachable at the same address.
So, while your router hands out private IPs to your devices at home, your ISP handles your public IP (either dynamically or statically).
What is a dynamic IP address?
A dynamic IP address is a temporary, automatically assigned IP that changes from time to time. Most home internet users have one by default. Your ISP leases it to you from a shared pool, and it might change when you restart your router, switch networks, or after a set period (like every 24 hours).
Because it’s not fixed, a dynamic IP doesn’t stay with your device forever. It’s like a hotel room; you use it for as long as you’re checked in, but once you leave, it’s reassigned to someone else.
How dynamic IPs work (DHCP protocol)
Dynamic IPs are assigned automatically using a system called DHCP, a process we covered earlier. Instead of manually requesting an IP, your device simply asks for one, and the DHCP server handles the rest.
Because these IPs come from a shared pool, they’re not tied to you for the long haul. You might keep the same one for days or weeks, but there’s no guarantee you’ll get it back after disconnecting (even briefly).
Example of a dynamic IP address
A dynamic IP address usually looks like a standard IPv4 format, something like 102.0.1.21, made up of four number blocks separated by dots. You’ve likely seen this kind of address before, even if you didn’t know what it meant.
It can range from 0.0.0.0 to a maximum of 255.255.255.255, but not all combinations are usable. Many are reserved for special purposes. But dynamic IPs are typically pulled from your ISP’s available public IP pool, which is large enough to support millions of users around the world.
Benefits of using a dynamic IP
Dynamic IPs come with several practical benefits, especially for casual internet users:
- Lower cost: They’re typically included in standard internet packages with no extra fees.
- More privacy: Since the IP changes periodically, it’s harder for trackers to follow your activity over time.
- Zero setup: Your device requests an IP automatically; no need to configure anything manually.
- Wider availability: ISPs have far more dynamic IPs than static ones, so they’re easier to assign.
- Beginner-friendly: Perfect for browsing, streaming, or social media without technical hassle.
Drawbacks of dynamic IPs
Despite their convenience, dynamic IPs aren’t always ideal, especially if you need a consistent connection or plan to host services:
- Not great for remote access: It’s harder to reach a home network or server if the IP keeps changing.
- Harder to allowlist: Services that use IP-based access controls may not work well with dynamic IPs.
- Poor fit for self-hosting: Websites or apps hosted on your device can become unreachable if your IP changes.
- Location accuracy may vary: Because IPs are pulled from a shared pool, they might not match your real-world location.
- Less reliable for gaming or streaming: IP changes during a session could interrupt gameplay or media streams, although it doesn't happen very often.
What is a static IP address?
A static IP address is an internet address that stays the same over time. Unlike dynamic IPs, which can change regularly, a static IP remains fixed, and that consistency makes it especially useful for things like hosting websites, setting up remote access, or running servers.
Static IPs are commonly used by businesses, but individual users can request one as well, usually for specific networking needs.
How static IPs are configured
If you want a static IP, you’ll typically need to request one from your ISP or network administrator. It often comes with an extra cost, since you’re asking for a dedicated address that won’t be reassigned to someone else.
Once assigned, a static IP can be configured in two ways:
- Automatically by your ISP or network admin, linking the IP to your router so that all connected devices use it.
- Manually on individual devices, by entering the IP details in your network settings.
If you need help setting it up, follow our step-by-step guide to configure a static IP address on routers, desktops (Windows, Mac, and Linux), and smartphones (Android and iOS).
Example of a static IP address
Static IP addresses look just like dynamic ones, something like 203.0.113.42. You can’t tell whether an IP is static or dynamic just by looking at it. The key difference is in how it’s assigned and whether it changes over time.
Advantages of a static IP
Static IPs offer benefits for specific use cases:
- Improved network security: You can allowlist certain IPs to restrict access to sensitive systems, which is great for businesses and remote teams.
- Reliable hosting: Hosting a website or server is easier with a fixed IP, since DNS servers always know where to find it.
- Stable VoIP and video calls: Services like Zoom and VoIP apps tend to be more reliable with a consistent IP address.
- Accurate geolocation: Since static IPs don’t change, services that rely on location data can usually pinpoint your region more reliably.
Disadvantages of static IPs
Despite the upsides, static IPs aren’t ideal for everyone:
- Additional cost: ISPs often charge extra for static IPs, sometimes a one-time fee, other times a monthly add-on.
- Less privacy: Because your IP doesn’t change, websites and trackers can more easily associate your activity with a single identity.
- Technical complexity: Unlike dynamic IPs handled automatically by DHCP, static IPs usually require manual configuration.
- Limited supply: The pool of available IPv4 addresses is shrinking, making static IPs harder to get, especially in regions or networks with high demand.
Differences between static and dynamic IP addresses
The choice between a static and dynamic IP depends on what you're trying to do. Here’s how they compare in terms of performance, reliability, security, and cost:
| Factor | Dynamic IP | Static IP |
| Status | Changes over time | Remains constant |
| Cost | Usually free | Usually paid |
| Setup complexity | Low | High |
| Privacy | Better | Easier to track |
| Stability | May fluctuate | Consistent |
| Hosting and DNS | Limited | Reliable |
| Remote access | Hard to maintain | Ideal |
| IP allowlisting | Not reliable | Fully supported |
| Geolocation | Varies | More accurate |
Should you use a static or dynamic IP?
Choosing between a static and dynamic IP address really comes down to how you use the internet.
If you're a casual user who mostly browses, streams, or games online, a dynamic IP is more than enough. It’s easy to manage, cost-effective, and offers decent privacy by default. You won’t need to lift a finger, as your ISP handles everything automatically.
But if you're hosting a website, accessing devices remotely, or managing secure business operations, a static IP might be worth the investment. It ensures consistent access and is easier to integrate into firewalls, VPNs, and DNS settings. Businesses often use static IPs to control who can connect to their internal systems, which is ideal for remote work setups.
In some cases, a hybrid approach makes sense: static IPs for critical devices and dynamic ones for everything else.
How to check if your IP address is static or dynamic
Static and dynamic IP addresses look the same, so you may be unable to tell the difference by simply looking at them. However, there are clever ways to tell both apart on smartphones and desktop computers.
Checking your private IP address
On Windows
- Click on the network icon. This could be Wi-Fi or Ethernet, depending on what you’re connected to.
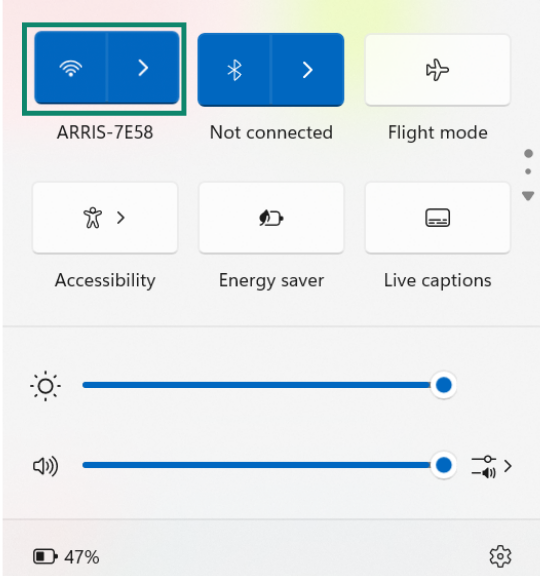
- Click Properties on the network you’re connected to.
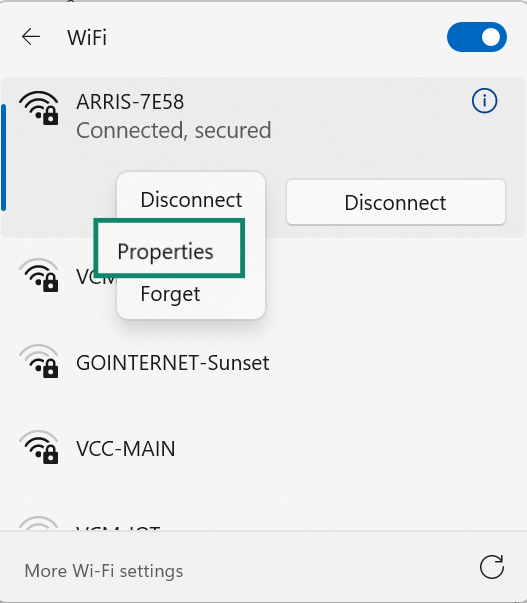
- Scroll to IP settings and look for IP assignment. If it’s set to Automatic (DHCP), you have a dynamic IP address. If it’s set to Manual, that means you’re using a static IP address.
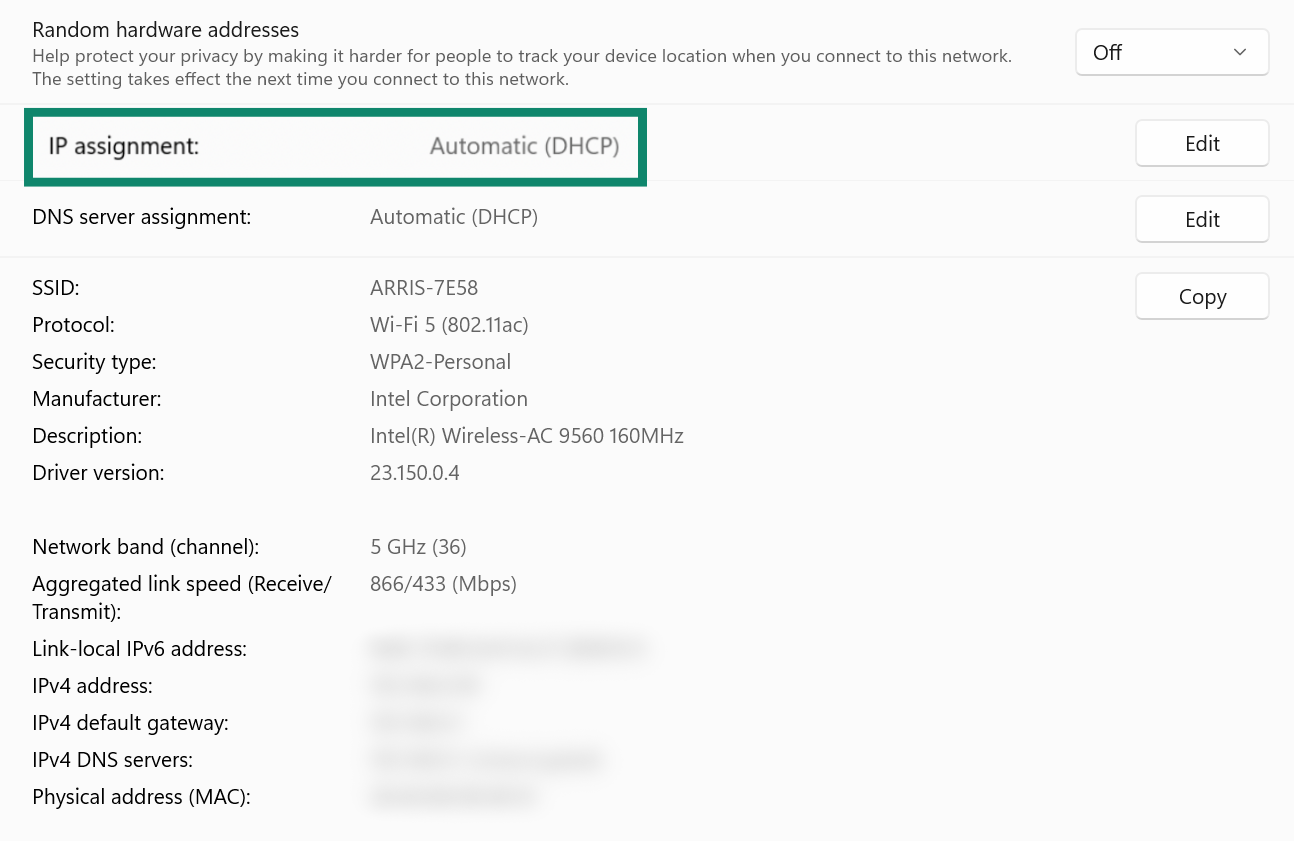
On Mac
- Click the Apple icon, then System Settings.
- Tap Network and pick your current connection (mine’s Wi-Fi).
- Click Details… next to the connected network.
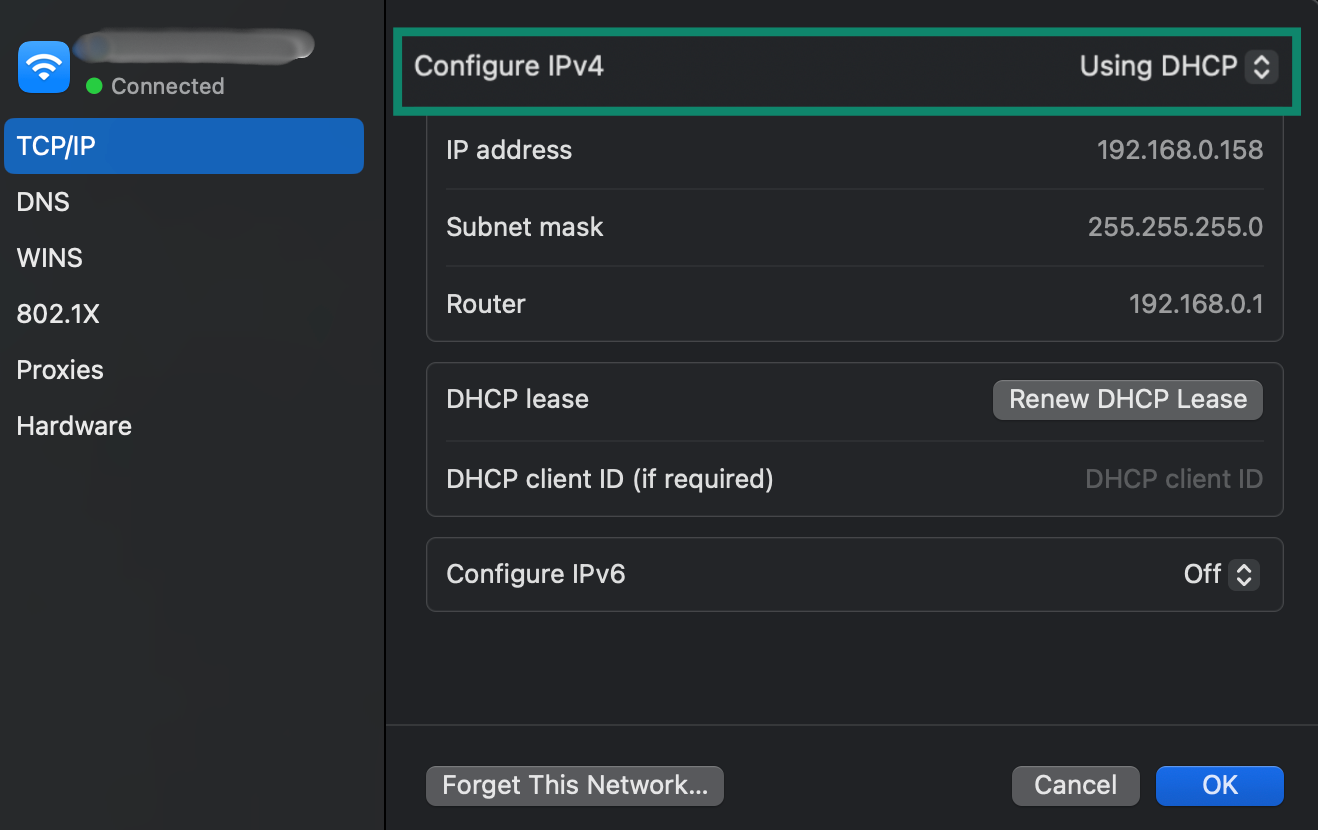
- Go to TCP/IP and check Configure IPv4. If it’s set to Using DHCP, your device has a dynamically assigned private IP address. If it’s set to Manually, then your device is using a static private IP.
On Android
-
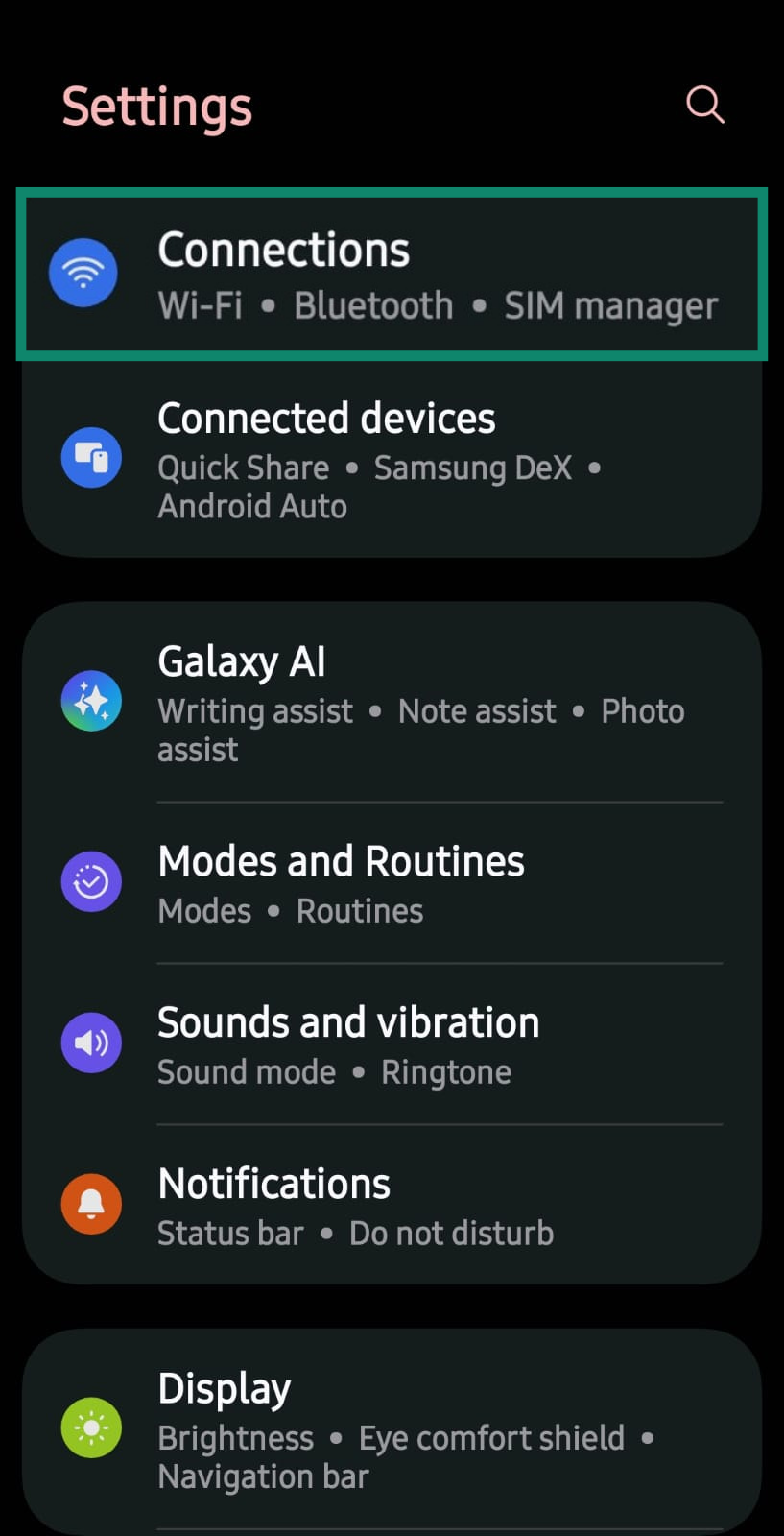
- Go to your Android device’s Settings and click Connections.
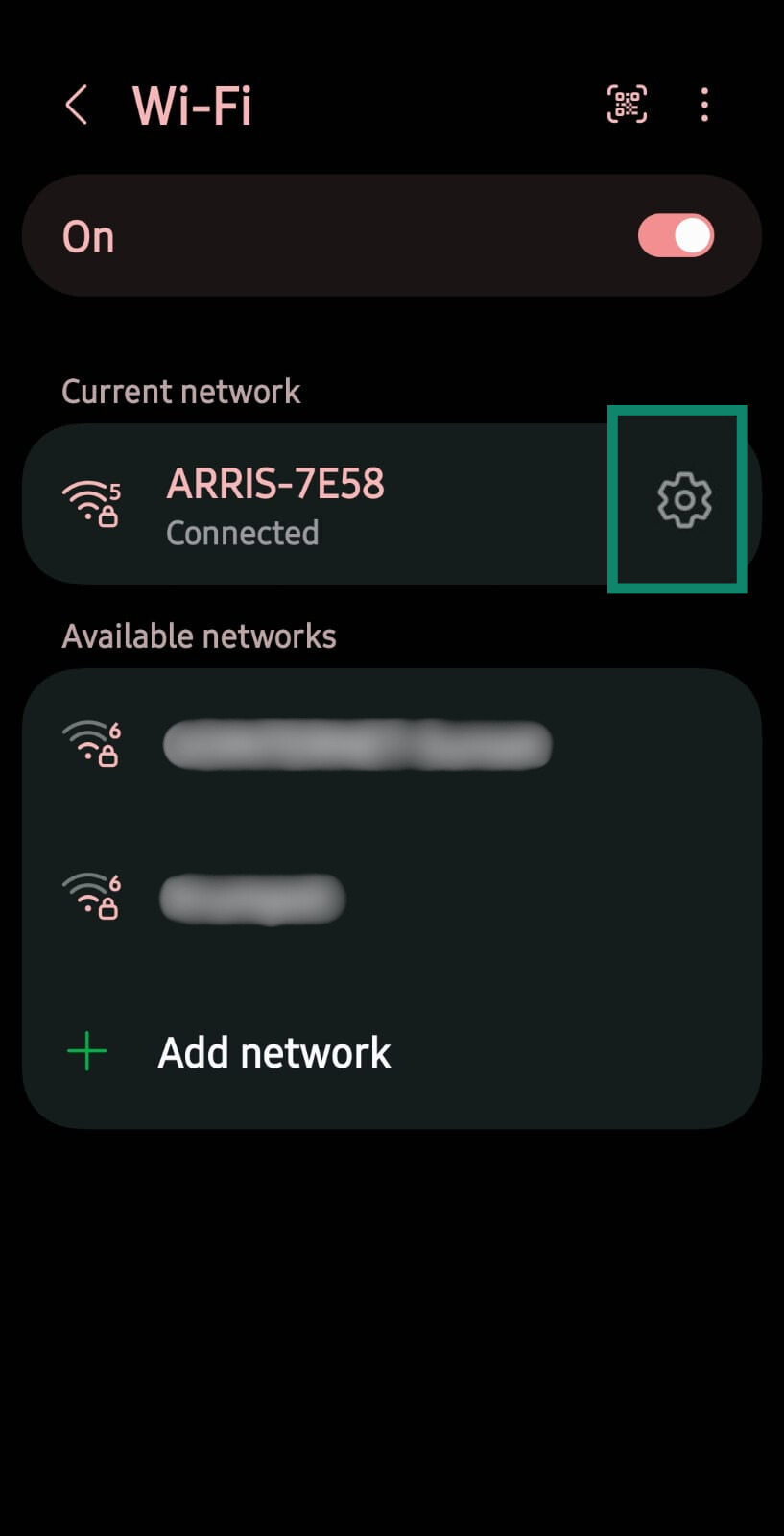
- Tap the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to and then the gear icon.
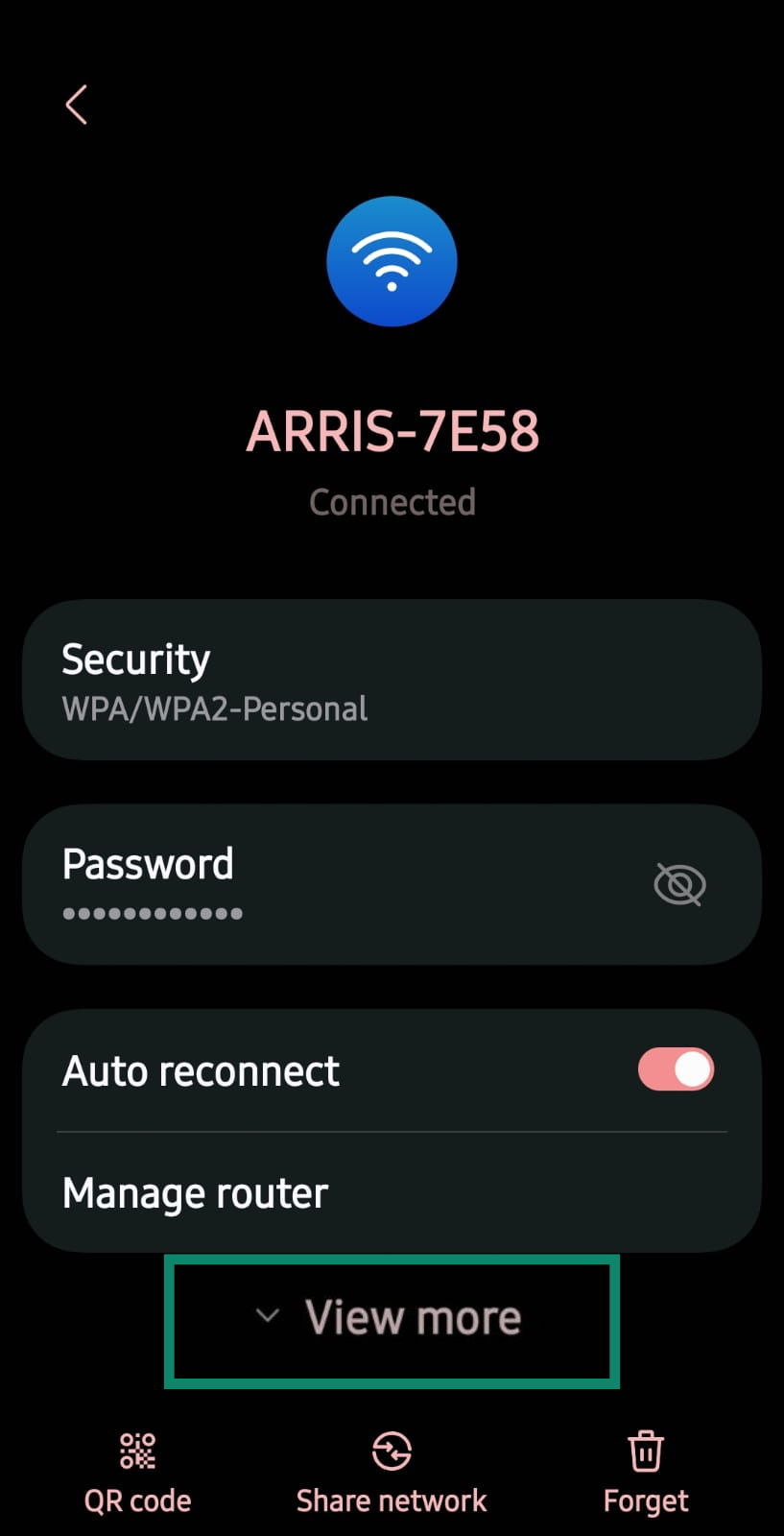
- Tap View more or continue scrolling to see more connection details.
- Look for IP Settings. If it says DHCP, you’re using a dynamic IP address. If it says Static, then it’s a static IP.
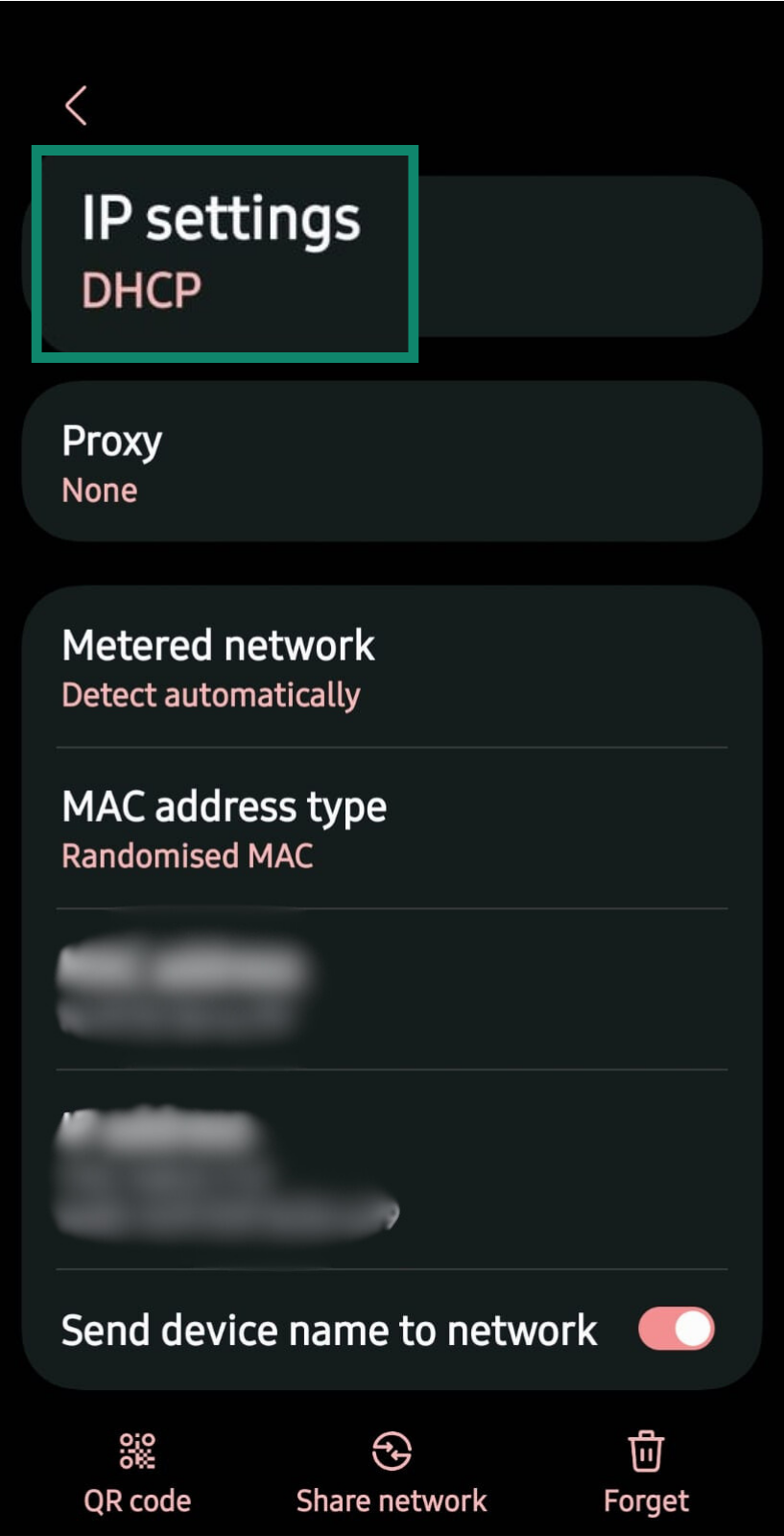
- Go to your Android device’s Settings and click Connections.
On iOS
- Go to your iOS device’s Settings and click Wi-Fi.
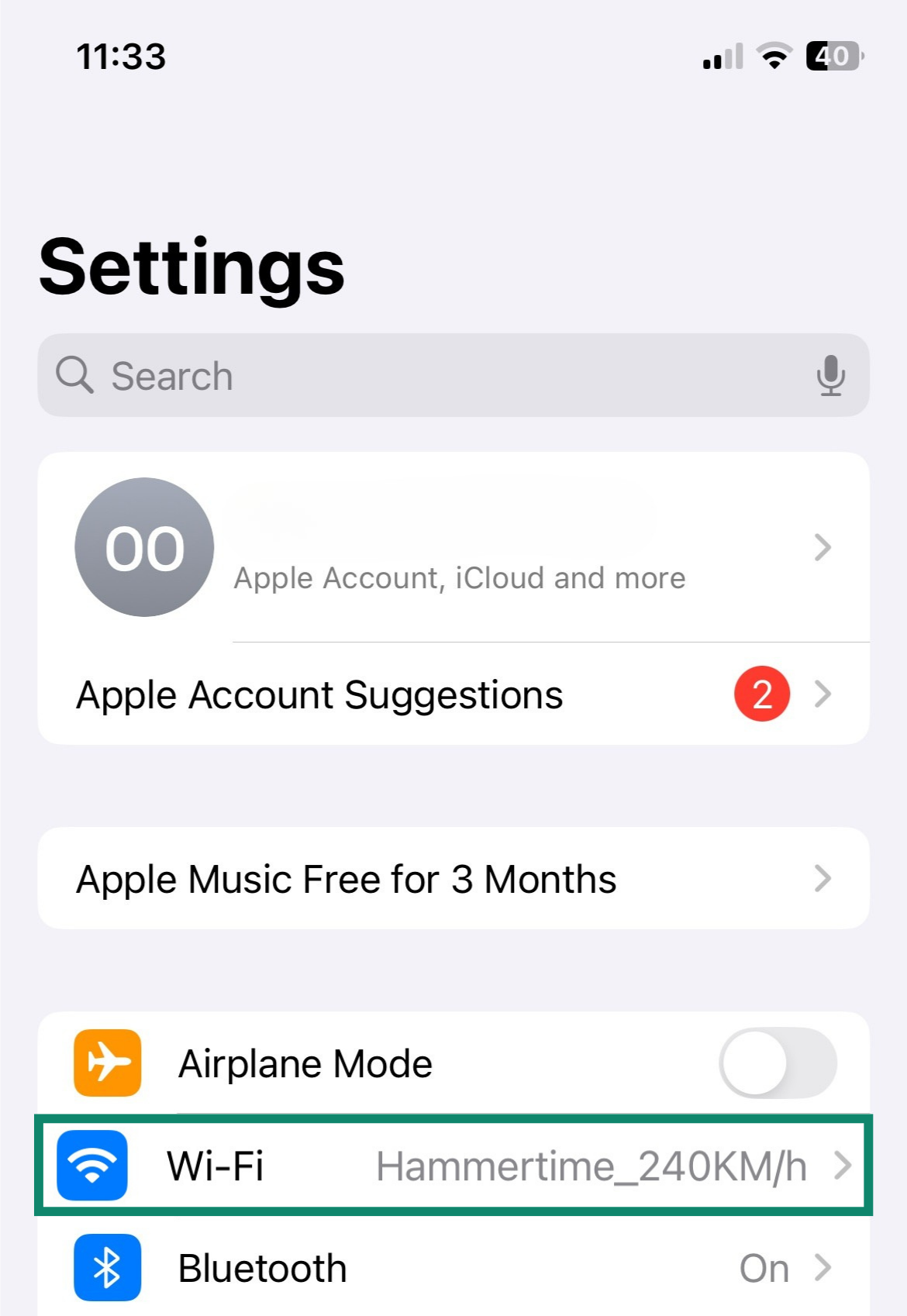
- Tap the current network you’re connected to.
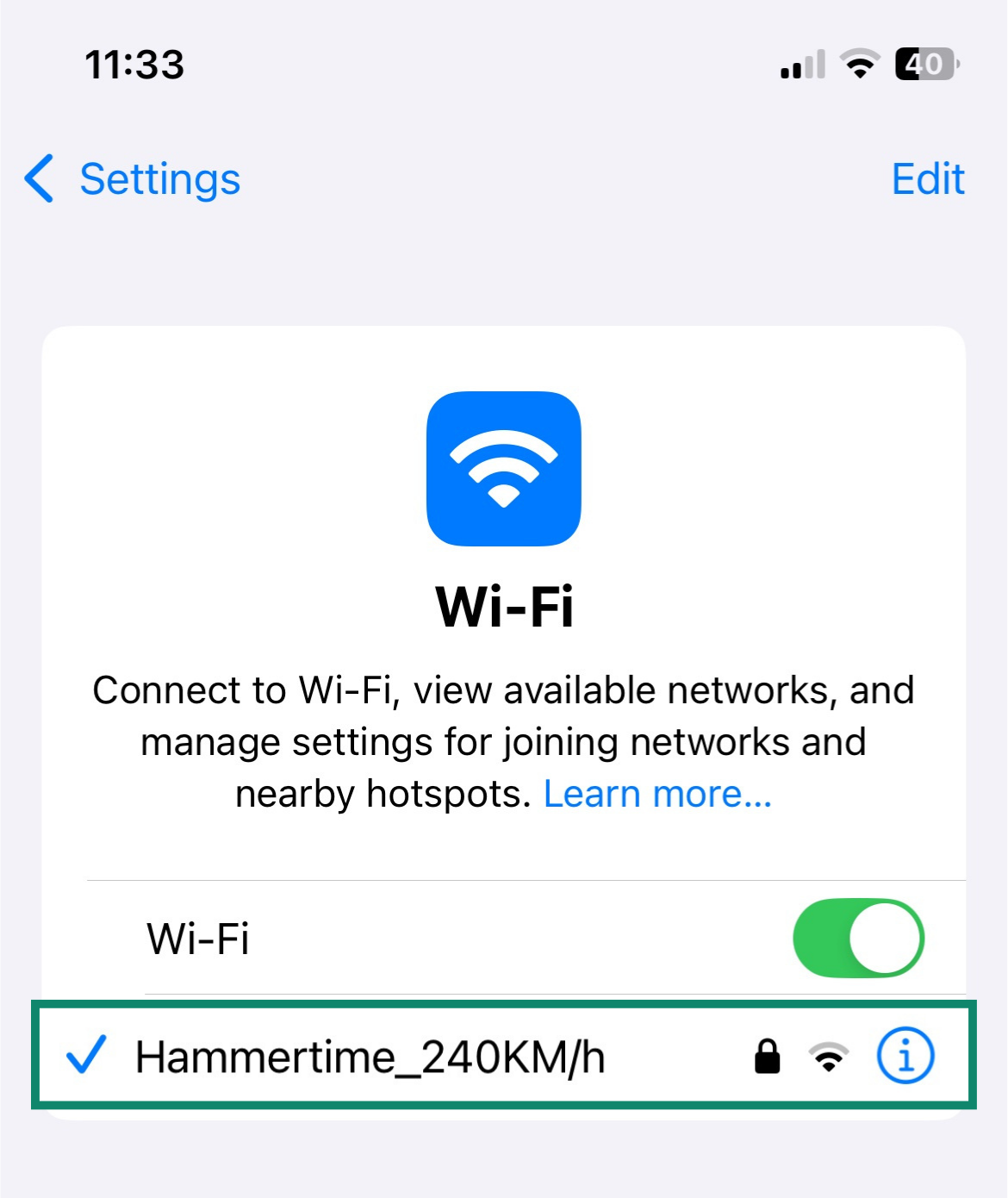
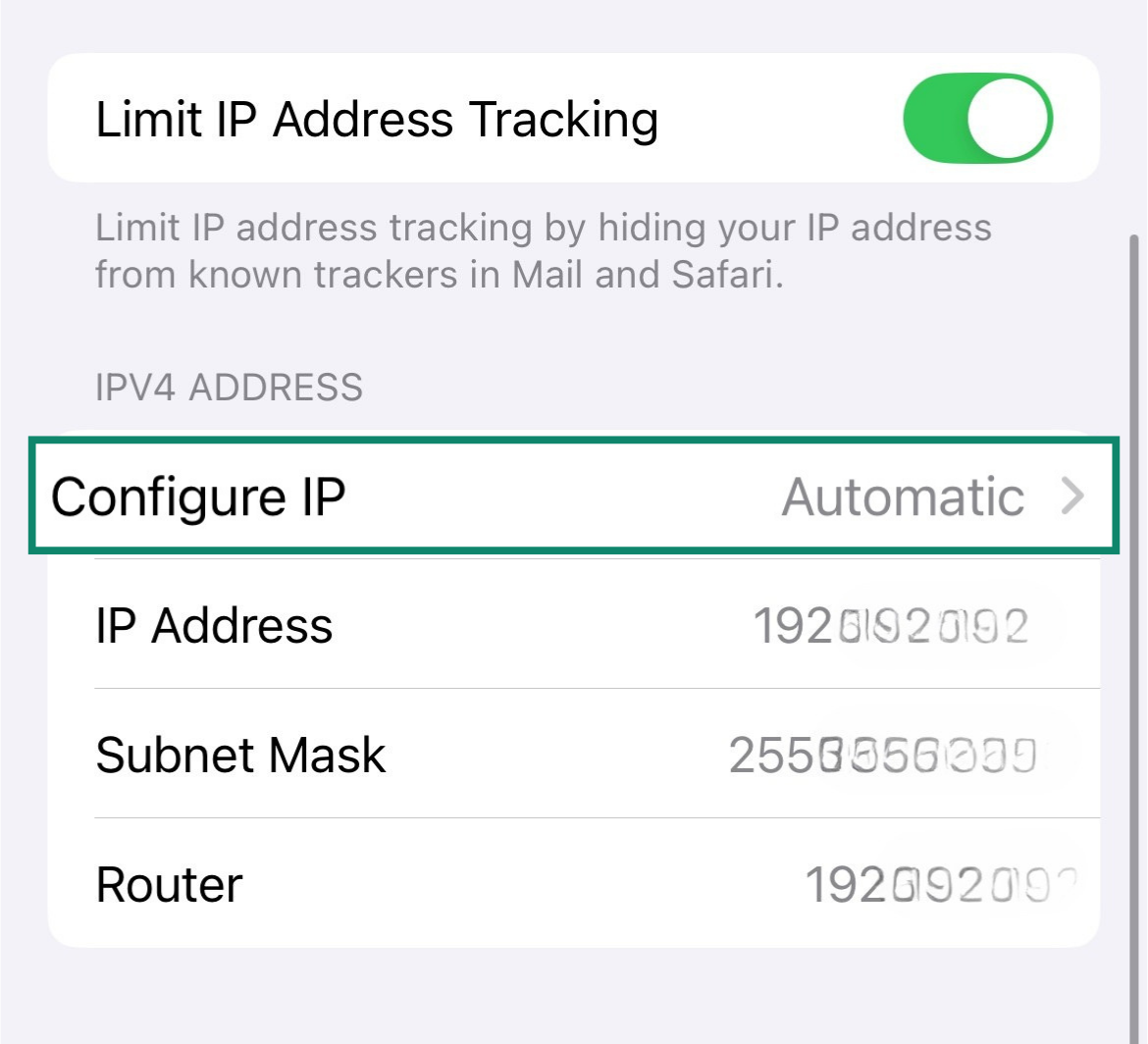
- Check for Configure IP. If it’s set to Automatic, then that’s a dynamic IP address. If it’s set to Manual, then you have a static IP address.
Checking your public IP address
To find out whether your public IP is static or dynamic:
- Check your current public IP address. Use ExpressVPN’s free IP address lookup tool to see your current IP.

- Restart your router. Unplug it for a minute, then plug it back in and reconnect.
- Check your IP again using the same tool. If your IP address changes, you're likely using a dynamic IP. If it stays the same, you might have a static IP (but it’s not guaranteed).
- For confirmation, contact your ISP or check your account dashboard. Static IPs usually cost extra.
How to get a static or dynamic IP address
There are a few ways to get either a static or dynamic IP address, depending on your needs and setup.
1. Requesting from your ISP
As mentioned before, most internet service providers assign dynamic IP addresses by default. You don’t need to configure anything; just sign up for a plan, and your device will be automatically assigned a dynamic IP via DHCP.
If you need a static IP, you’ll usually have to request it directly from your ISP. While it’s called “static,” your ISP may still use DHCP behind the scenes, reserving a specific IP for your account so it always stays the same. This typically doesn’t require any manual setup on your end, but some ISPs may charge extra for this service.
2. Using a VPN with static or dynamic IP options
If you’d like to change your IP address more frequently or choose an IP in another country, you can use a VPN.
VPNs like ExpressVPN let you change your IP address quickly and easily. When you connect to any of ExpressVPN’s 100+ server locations, you're assigned a dynamic IP from that region. Reconnecting gives you a new one, which helps protect your privacy by making your activity harder to track.
ExpressVPN even offers the ShuffleIP feature (IP rotation), where your IP changes automatically with every new request for added privacy.
If you need something more consistent, ExpressVPN also offers dedicated IP addresses. A dedicated IP works just like any other VPN connection, but you’ll keep the same IP address every time you connect, tied to a location of your choice.
How to protect your IP address and prevent IP tracking
Your IP address might not reveal your exact home address, but it can still expose plenty, like your general location, online behavior, or network identity. In the wrong hands, it can be used for:
- Approximating your location to a specific city or neighborhood.
- Launching DDoS attacks that flood your connection and knock you offline.
- Being added to dark web data dumps, especially when combined with leaked credentials.
- Letting snoopers (like employers or ISPs) track your browsing activity.
- Getting blocklisted if someone uses your IP for spamming or abuse.
- Framing you by masking illegal online activity behind your IP.
Curious how this works? Check out more details on what someone can do with your IP address and how IP addresses can be traced.
So how can you keep your IP address private and reduce your exposure? Here are two of the most effective ways:
- Use a VPN to hide your IP: The most effective way to protect your IP address is by using a VPN. A VPN routes your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel and replaces your real IP address with one from a different location. This masks your true location, prevents tracking, and keeps your online activity private.

- Secure your network with a firewall: A strong home network setup plays a key role in IP protection. Firewalls help block unauthorized access to your local network, prevent external probing, and reduce the risk of unwanted connections from the internet.
FAQ: Common questions about static and dynamic IPs
Which is better: static or dynamic IP?
Dynamic IPs are better for regular internet users since they’re easier to set up, more affordable, and handle a wide range of everyday internet tasks without hassle. However, a static IP address is better for remote access management, improved port forwarding, and business setups.
How do I know if my IP address is static or dynamic?
If you check your device’s network settings, you’re usually seeing how your private IP address is assigned within your local network. If it’s set to automatic (using DHCP), it’s a dynamic IP. If it’s manually configured, it’s static.
However, this doesn’t tell you whether your public IP address is static or dynamic. To check that, you’ll typically need to restart your router and see if your IP changes or contact your ISP directly for confirmation.
What are the benefits of a static IP address?
Static IP addresses are beneficial for businesses looking to improve network stability and reliability. Static IPs also make it easier to set up allowlisting, ensuring remote access to internal network resources from only trusted computers.
What is the difference between static and dynamic IP allocation?
Dynamic IP addresses are typically assigned automatically using the DHCP protocol, making them easy to manage and ideal for most everyday users. Static IP addresses, on the other hand, are manually assigned or reserved for a specific device, so they always stay the same.
Is dynamic IP the same as PPPoE?
Dynamic IP isn’t the same as PPPoE. Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet defines how your devices connect to your internet modem and has nothing to do with the state of your IP addresses.
Which IP type is better for gaming or remote work?
Static IP addresses are generally better for remote work, especially if you need secure and consistent access to company networks or services.
For gaming, a static IP can help with stability and port forwarding, particularly if you’re hosting or need to connect to the same servers regularly. That said, a dynamic IP might be safer for everyday gamers, as it makes you less vulnerable to targeted DDoS attacks.
Can I switch between static and dynamic IP?
Yes, you can switch between static and dynamic IPs. It’s easy with a VPN; connecting to a regular VPN server gives you a dynamic IP, while some VPNs (like ExpressVPN) offer dedicated static IPs if you need a consistent address. No need to go through your ISP or change settings manually.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN